Stepper motors, a fascinating subset of electromechanical devices, have revolutionized the way precise rotational movements are achieved. Their unique ability to divide a full rotation into discrete steps allows for accurate position control, making them indispensable in various industries. In this blog, we’ll delve into the workings of stepper motors, their types, advantages, and applications, as well as explore the different types of stepper motor drives and factors to consider when selecting the appropriate motor for specific applications.
Table of Contents
ToggleDefinition of Stepper Motor:
Stepper motors are synchronous motors that transform electrical pulses into mechanical movement. The rotation of the motor occurs in equal and fixed steps, providing precise control over its position.
Types of Stepper Motor:
These stepper motors are three types. One of them is a permanent magnet and other is Variable Reluctance Stepper Motors and the third is a combination of both.
Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor:
The most commonly used type, these motors have a permanent magnet rotor and offer reliable performance in numerous applications.
Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor:
Utilizing a toothed rotor, these motors rely on the principle of minimum reluctance for their operation.
Hybrid Stepper Motor:
Combining features of permanent magnet and variable reluctance motors, hybrid motors provide enhanced performance and versatility.
How Stepper Motor Works:
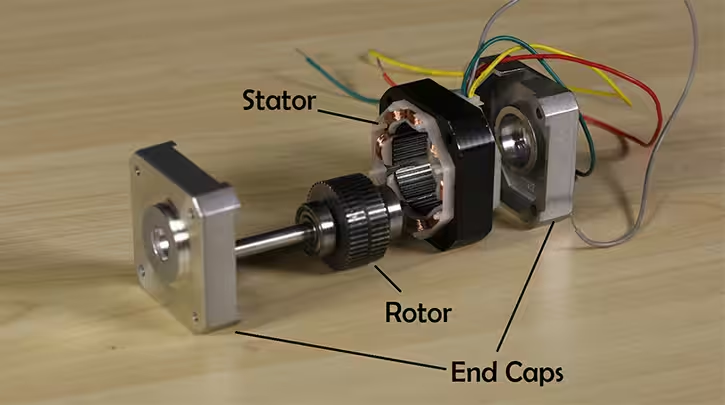
Stepper motors operate based on the principles of electromagnetism. The stator contains windings that, when energized in a specific sequence, create a magnetic field. The rotor, either permanent magnet or toothed, aligns with the stator’s magnetic field, resulting in rotational movement.
Steps, Poles, and Phases:
The number of steps, poles, and phases in a stepper-motor affects its operation and resolution. More steps and poles lead to smoother motion and finer positioning, while more phases enhance the motor’s torque and efficiency.
Advantages of Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors offer several key advantages:
- Precise Positioning: Their ability to move in discrete steps allows for accurate positioning without the need for feedback devices.
- Open-loop Control: Stepper motors can be controlled in an open-loop fashion, simplifying the control system and reducing costs.
- No Feedback Required: Unlike servo motors, stepper motors do not require continuous feedback to maintain position accuracy.
- Cost-effectiveness: Stepper motors are relatively economical compared to other motor types, making them suitable for various applications.
Types of Stepper Motors Drives:
Stepper motors require electronic circuits known as motor drives to control their movement. The main types of drives are:
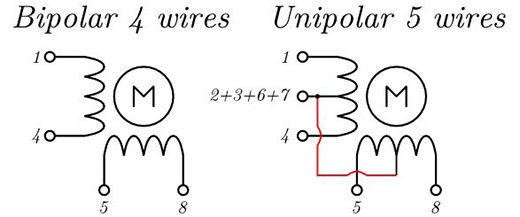
Unipolar Drive: Utilizing two separate windings per phase, the unipolar drive is simple to implement but may have lower efficiency and power output.
Bipolar Drive: Treating each winding as an independent coil, the bipolar drive offers better performance and efficiency, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Half-step vs. Full-step Drive: Full-step drives provide more torque, while half-step drives offer smoother motion and finer positioning due to smaller step sizes.
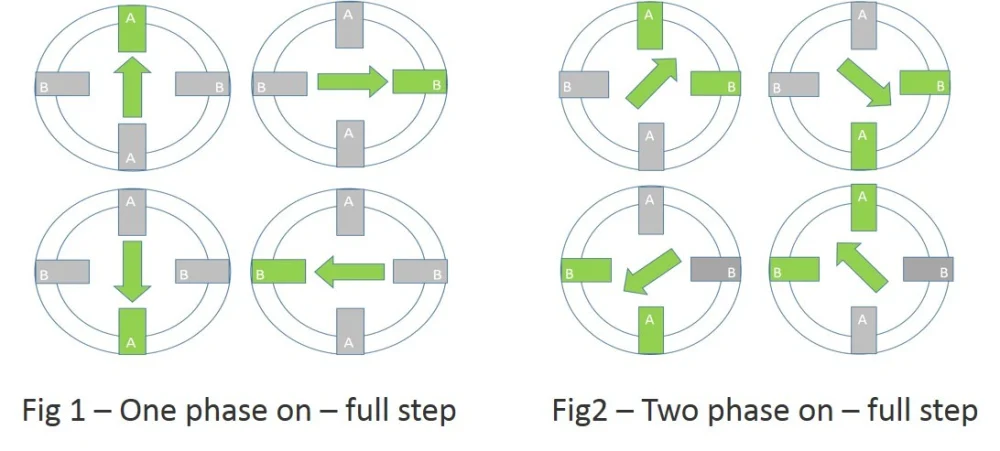
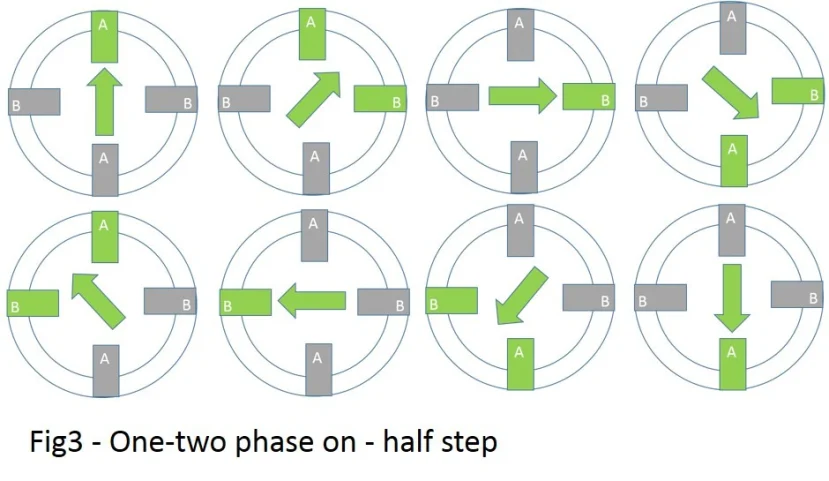
You can also visit this portal for a more detailed explanation of Half step, Full step & Micro steps of the stepper motor.
Applications of Stepper Motors:
- CNC Machines and 3D Printers for precise control of tool movements.
- Robotics and Automation for accurate positioning and movement.
- Camera Autofocus Mechanisms for smooth and accurate focus adjustments.
- Disk Drives for precise head positioning.
Stepper Motor Selection Criteria:
- When choosing a stepper motor for a specific application, consider:
- Torque Requirements: Ensure the motor can handle the required load.
- Speed Considerations: Choose a motor with the appropriate speed characteristics.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Match the motor’s ratings with the power supply.
- Environmental Factors: Consider factors like temperature and humidity to ensure reliable performance.
In conclusion, stepper motors have become an indispensable tool for achieving precise control of rotational movements in various industries. With their numerous advantages, diverse applications, and different driving options, stepper motors continue to play a crucial role in advancing technology and automation across the globe.
You can also watch our “Stepper Motor Video” for more details.
Happy Learning..
Join Us on Social Media
Facebook: Automation Minds (https://www.facebook.com/plcdcscontrol)
LinkedIn: Automation Minds (https://www.linkedin.com/company/plcdcscontrol)
YT: Automation Minds (https://youtube.com/@AutomationMinds)
Visit our blog to understand Modbus open protocol