In the ever-evolving landscape of technology and automation, SCADA systems have emerged as indispensable tools across a wide range of industries. Standing for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, SCADA system plays a pivotal role in real-time monitoring, control, and data analysis. In this blog, we will delve into the core components, architecture, applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends of SCADA system, focusing on their versatile applications across industries.

Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding SCADA Systems
At its heart, a SCADA system comprises several key components working in tandem. Supervisory control involves the centralized control and management of various processes. Data acquisition involves the collection of real-time data from multiple sensors and devices. The Human-Machine Interface (HMI) facilitates communication between operators and the system. Remote terminal units (RTUs) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) serve as the interface between physical devices and the SCADA software. Communication protocols, such as Modbus or DNP3, ensure seamless data exchange between various components.
SCADA Architecture and Functionality
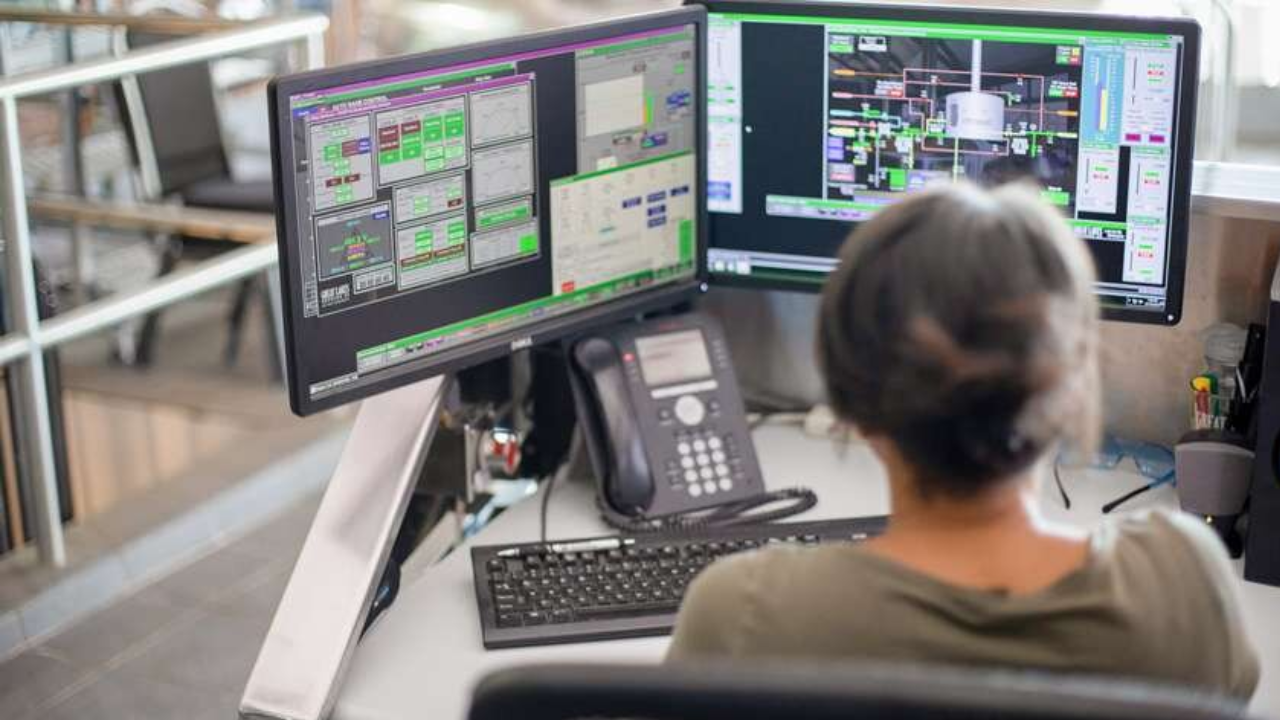
The architecture of a SCADA system typically follows a hierarchical structure. At the base level, sensors and devices collect data, which is then transmitted to the RTUs or PLCs. These devices, in turn, forward the data to the central server. The HMI allows operators to visualize and interact with the data. SCADA system enable real-time monitoring, remote control, and data analysis, facilitating informed decision-making.

Industries and Sectors Utilizing SCADA Systems
The applications of SCADA systems span across diverse industries. In the energy and utilities sector, SCADA is instrumental in managing power generation, distribution, and consumption. It also plays a crucial role in water treatment and distribution, optimizing resource utilization. In manufacturing, SCADA ensures quality control by monitoring production processes and automating tasks. Similarly, in transportation, SCADA system oversee traffic management, monitor railway systems, and ensure smooth operations.
In the oil and gas industry, SCADA system is vital for monitoring and controlling vast pipeline infrastructures, often located in remote areas. This not only ensures efficient distribution but also enhances safety by detecting leaks and faults promptly.
Watch our YouTube Video for SCADA Explanation (in Hindi)
Benefits of SCADA Systems
The advantages of implementing SCADA systems are numerous. Operational efficiency is greatly improved through automation, reducing human intervention and potential errors. Real-time monitoring capabilities enable quick response to anomalies, minimizing downtime. The early detection of faults and predictive maintenance enhance equipment longevity and reduce maintenance costs. Furthermore, the data collected by SCADA systems empower organizations to make data-driven decisions and perform trend analysis.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, SCADA systems come with their own set of challenges. Security is a paramount concern, as these systems are potential targets for cyberattacks. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is imperative to safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, integrating SCADA systems with existing legacy systems and technologies can be complex, requiring careful planning and execution. As industries expand, scalability becomes crucial, necessitating adaptable and scalable SCADA solutions.
Future Trends in SCADA Systems
Looking ahead, several trends are shaping the evolution of SCADA system. The integration of SCADA with IoT devices is enabling a more interconnected and data-rich environment. Cloud-based SCADA systems are gaining traction, offering flexibility and accessibility. Advanced data analytics and predictive maintenance are enhancing the capabilities of SCADA systems, enabling proactive problem-solving. Amid the rapid technological advancements, a continued focus on cybersecurity remains paramount.
Case Study: SCADA in Energy Distribution
A prominent example of SCADA application is in energy distribution. SCADA system enables real-time monitoring of power generation, transmission, and distribution. Operators can remotely control substations, balance loads, and detect power outages promptly. This results in efficient energy distribution, reduced downtime, and improved customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SCADA systems have transformed industries by enabling efficient monitoring, control, and analysis of processes. Their versatile applications across energy, manufacturing, transportation, and more demonstrate their significance. As technology evolves, SCADA systems will continue to adapt, embracing trends such as IoT integration and advanced analytics. By understanding the capabilities and challenges of SCADA system, industries can harness their potential for improved operations and enhanced decision-making. The realm of SCADA applications is vast and ever-expanding, promising a future of increased automation and efficiency.
Read more for MQTT protocol