A boiler pressure relief valve is a critical component in ensuring the safe operation of boiler systems across various industries. These valves serve a vital role in preventing potentially catastrophic accidents by releasing excess pressure from the boiler system. In this section, we will provide a brief overview of the importance of boiler pressure relief valves and establish the purpose of this discussion, which is to delve into their functioning, significance, and the crucial need for regular maintenance.

Table of Contents
ToggleBrief overview of the importance of boiler pressure relief valves
Boiler systems operate under high pressure to generate steam for heating, power generation, and various industrial processes. However, if the pressure within the boiler exceeds safe limits, it can lead to devastating consequences such as explosions or ruptures. Boiler pressure relief valves act as a safety mechanism to prevent such scenarios by releasing excess pressure when it reaches predetermined thresholds.
These valves are designed to open automatically when the pressure surpasses a specified level, allowing steam or water to escape from the system until the pressure returns to a safe range. By doing so, they protect the integrity of the boiler, associated equipment, and most importantly, the safety of personnel working in proximity to the boiler.
Understanding Boiler Pressure Relief Valves: Definition and purpose
Boiler pressure relief valves are safety devices installed in boiler systems to mitigate the risk of catastrophic failure due to excessive pressure buildup. These valves are designed to automatically open when the pressure within the boiler surpasses a predetermined threshold, allowing steam or water to escape until the pressure returns to safe levels.
The primary purpose of boiler pressure relief valves is to protect the integrity of the boiler, associated piping, and equipment by preventing over pressurization. By releasing excess pressure, these valves prevent potentially disastrous situations such as explosions or ruptures, which could cause extensive damage to property and pose serious risks to personnel.
Legal and regulatory requirements:
Boiler pressure relief valves are subject to stringent legal and regulatory requirements aimed at ensuring the safety and integrity of boiler systems. These mandates vary depending on the jurisdiction and may include specific standards and guidelines that dictate the design, installation, and maintenance of pressure relief valves in boiler systems.
Regulatory bodies, such as occupational safety agencies or boiler inspection authorities, often enforce these requirements to prevent accidents and protect the well-being of workers and the public. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in penalties, fines, or even legal consequences for organizations responsible for operating and maintaining boiler systems.
Furthermore, industry standards and codes, such as those established by organizations like the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) or the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors (NBBI), provide additional guidance on the proper selection, installation, and maintenance of boiler pressure relief valves.
Adherence to legal and regulatory requirements is paramount in ensuring the effectiveness and reliability of boiler pressure relief valves, thereby safeguarding both personnel and assets from the potential hazards associated with boiler operation.
How Do Pressure Relief valves Work?
Type of Pressure Relief Devices:
First of all we should know the types of pressure relief devices. These are…
- Re-closing devices
- Direct Load
- Spring Loaded
- Weight Loaded
- Controlled
- Controlled safety pressure relief system
- Pilot operated safety pressure relief system
- Direct Load
- Non reclosing devices
- Rapture Disks
- Pin actuated devices
Here in this blog, we will discuss reclosing pressure relief devices.
Mechanism of operation (re closing devices):
Boiler pressure relief valves operate on a simple yet effective principle to release excess pressure and prevent catastrophic failures within boiler systems. The mechanism of operation involves a spring-loaded valve that remains closed under normal operating conditions. However, when the pressure within the boiler surpasses a predetermined threshold, the valve is forced open, allowing steam or water to escape.
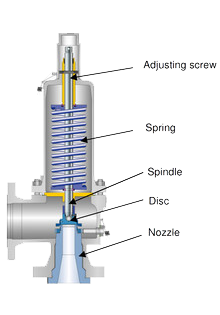
The pressure relief valve consists of a valve disk or piston, which is held against the valve seat by a spring. Under normal operating conditions, the force exerted by the spring keeps the valve tightly closed, preventing the escape of steam or water. However, as the pressure within the boiler increases beyond the set limit, the force exerted by the pressure on the valve disk overcomes the opposing force of the spring, causing the valve to lift and open.
Once the valve is open, excess pressure is relieved as steam or water is discharged from the boiler system. As the pressure decreases and returns to safe levels, the force exerted by the spring eventually closes the valve, restoring the system to its normal operating state.
The mechanism of operation ensures that boiler pressure relief valves respond swiftly and effectively to sudden pressure surges, providing essential protection against the risks of over pressurization.
Pressure thresholds:
Boiler pressure relief valves are designed to activate at predetermined pressure thresholds, which are carefully selected based on the operating parameters and safety requirements of the boiler system. These pressure thresholds are typically determined during the design and installation of the valve, taking into account factors such as the maximum allowable working pressure of the boiler and the capacity of the relief valve.
The predetermined pressure levels at which the valve activates are critical for ensuring the safety and integrity of the boiler system. If the pressure relief valve were to activate at pressures too low, it might unnecessarily discharge steam or water, leading to energy wastage and potential operational inefficiencies. Conversely, if the pressure relief valve were to activate at pressures too high, it might fail to relieve excess pressure effectively, putting the system at risk of over pressurization.
Therefore, the pressure thresholds of boiler pressure relief valves are carefully calibrated to provide optimal protection while minimizing the likelihood of false activations or inadequate pressure relief. By adhering to these predetermined pressure levels, boiler pressure relief valves play a crucial role in maintaining the safety and reliability of boiler systems in various industrial applications.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the proper functioning of boiler pressure relief valves. Several maintenance tasks are necessary to keep these valves in optimal condition and mitigate the risk of failure. Some of the key maintenance activities include:
Visual inspections: Regular visual inspections should be conducted to check for signs of damage, corrosion, or leakage on the pressure relief valve and its associated components. Inspectors should look for any signs of wear on the valve seat, disc, or spring, as well as any indications of leakage around the valve body or connections.
Testing: Periodic testing of pressure relief valves is crucial to verify their functionality and ensure they operate within specified parameters. Testing typically involves simulating overpressure conditions to confirm that the valve opens at the designated pressure threshold and closes properly once the pressure returns to normal levels.
Cleaning: Over time, pressure relief valves may accumulate dirt, debris, or scale deposits that can interfere with their operation. Regular cleaning of the valve and its components is necessary to remove any obstructions and ensure unimpeded movement of the valve disc or piston.
Adjustment: In some cases, pressure relief valves may require adjustment to maintain optimal performance. This may involve calibrating the spring tension or adjusting the set pressure to align with the operational requirements of the boiler system.
Record-keeping: It’s essential to maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities performed on pressure relief valves, including inspection findings, test results, and any adjustments made. These records help track the valve’s performance over time and facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements.
By implementing a comprehensive maintenance program that includes these tasks, industries can ensure the reliability and effectiveness of boiler pressure relief valves, thereby enhancing overall safety within the boiler system.
Risks of neglecting its maintenance
Neglecting the maintenance of pressure relief valves can have serious consequences for boiler safety and reliability. Some of the potential risks associated with failing to maintain pressure relief valves include:
Failure to relieve excess pressure: If a pressure relief valve becomes blocked or impaired due to lack of maintenance, it may fail to open when needed, resulting in the inability to relieve excess pressure from the boiler system. This increases the risk of over pressurization, which can lead to boiler explosions or ruptures.
Reduced efficiency: Accumulation of dirt, debris, or scale deposits on the pressure relief valve can restrict its movement and impair its ability to function properly. As a result, the valve may operate inefficiently or inaccurately, leading to energy wastage and potential operational inefficiencies.
Compliance issues: Failure to maintain pressure relief valves in accordance with regulatory requirements can result in non-compliance with safety standards and regulations. This may subject organizations to penalties, fines, or legal consequences for failing to uphold the necessary safety measures.
Safety risks: Perhaps most importantly, neglecting the maintenance of pressure relief valves poses significant safety risks to personnel working in proximity to the boiler system. Without proper maintenance, the likelihood of boiler accidents, injuries, and fatalities increases, jeopardizing the well-being of workers and the surrounding environment.
The risks of neglecting the maintenance of boiler pressure relief valves are far-reaching and can have serious implications for safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Therefore, prioritizing regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the continued safe and reliable operation of boiler systems.
Maintenance Procedures of pressure relief valves
Visual inspections:
Visual inspections are a fundamental aspect of boiler pressure relief valve maintenance.
Testing:
Testing pressure relief valves is crucial to ensure their functionality and compliance with safety standards. Here’s an overview of the process:
Prepare for Testing: Ensure that the boiler system is safely shut down, depressurized, and cooled before proceeding with the test.
Set Up Test Equipment: Use appropriate testing equipment, such as a pressure gauge and testing apparatus, to simulate overpressure conditions in the boiler system.
Apply Pressure: Gradually increase the pressure in the testing apparatus to the predetermined set point of the pressure relief valve being tested.
Observe Valve Operation: Monitor the pressure relief valve during the test to verify that it opens at the specified pressure threshold and releases excess pressure as intended. Document the test results, including the pressure at which the valve activates and any observations regarding its performance, in the maintenance log for future reference.
Reset and Reassemble: Once the test is completed, reset the pressure relief valve to its normal operating position and reassemble any components that were disassembled for testing.
Regular testing of pressure relief valves helps ensure their reliability and effectiveness in protecting the boiler system from overpressure conditions.
Replacement:
Pressure relief valves may need to be replaced under certain circumstances when maintenance is no longer sufficient to ensure their proper functioning. Here’s when and why replacement may be necessary:
Wear or Damage: If visual inspections or testing reveal significant wear, corrosion, or damage to the pressure relief valve components that cannot be addressed through maintenance, replacement may be necessary to restore the valve’s effectiveness.
Failed Testing: If pressure relief valves fail to operate within specified parameters during testing, indicating potential deficiencies in their performance, replacement may be warranted to ensure the safety and reliability of the boiler system.
Obsolete or Non-Compliant Valves: In some cases, pressure relief valves may need to be replaced to comply with updated safety standards or regulatory requirements, particularly if the existing valves are outdated or no longer meet current industry standards.
End of Service Life: Pressure relief valves have a finite service life, and replacement may be necessary as they approach the end of their operational lifespan to maintain the integrity and safety of the boiler system.
When replacing pressure relief valves, it’s essential to select valves that meet the required specifications and comply with applicable safety standards and regulations. Additionally, proper installation and calibration are crucial to ensure the new valve functions effectively within the boiler system.
Digital Pressure relief valve:
An electronic pressure control valve is a sophisticated device used in various industrial applications to precisely regulate and maintain pressure levels within a system. Unlike traditional mechanical pressure control valves, electronic pressure control valves utilize electronic components such as sensors, actuators, and microprocessors to monitor and adjust pressure with a high degree of accuracy and responsiveness.
The operation of an electronic pressure control valve involves continuously sensing the pressure within the system using built-in sensors. These sensors provide real-time feedback to the electronic control unit, which processes the data and determines the appropriate action required to achieve the desired pressure setpoint.
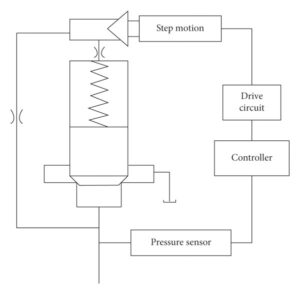
Based on the input from the sensors and programmed algorithms, the control unit signals the actuator to adjust the valve opening accordingly. This allows the valve to modulate its flow rate, thereby regulating the pressure within the system to match the predefined setpoint.
One of the key advantages of electronic pressure control valves is their ability to offer precise control over a wide range of operating conditions. They can respond rapidly to changes in pressure demand, making them ideal for applications where maintaining tight pressure tolerances is critical.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the importance of regular maintenance cannot be overstated when it comes to preserving the effectiveness of boiler pressure relief valves. These valves serve as critical safety components, protecting boiler systems and personnel from the potentially catastrophic consequences of overpressure situations. However, without proper maintenance, their ability to function optimally may be compromised, increasing the risk of accidents and failures.
By conducting routine visual inspections, testing, cleaning, and replacement as needed, industries can ensure that pressure relief valves remain in peak condition and capable of promptly responding to overpressure events. Regular maintenance helps identify and address issues before they escalate, safeguarding the integrity and reliability of boiler systems over time.
It is imperative for industries to prioritize boiler safety through proactive maintenance of pressure relief valves. This involves not only complying with legal and regulatory requirements but also going above and beyond to implement comprehensive maintenance programs aimed at maximizing the reliability and effectiveness of these critical safety devices.
We urge industries to allocate resources and dedicate personnel to the regular inspection, testing, and maintenance of pressure relief valves as part of their overall boiler safety protocols. By investing in proactive maintenance practices, industries can mitigate the risks of boiler accidents, protect personnel and assets, and ensure uninterrupted operations.
Let us collectively commit to upholding the highest standards of safety in boiler systems by prioritizing the maintenance of pressure relief valves. Together, we can create safer work environments, prevent costly disruptions, and ultimately save lives.
FAQs
Question: What is the Purpose of a Safety Valve?
Answer: The primary function of a safety valve is to safeguard lives, property, and the environment. These valves are specifically engineered to open when pressure within vessels or equipment exceeds safe limits, releasing the excess pressure, and then automatically closing afterward.
Question: How Does a Safety Valve Operate?
Answer: Safety valves function differently based on their design and intended use. The three main types of safety valves include spring-loaded, weight-loaded, and controlled safety valves. Each type operates uniquely to ensure pressure regulation and prevent dangerous overpressure situations.
Question: What is the Set Pressure of a Safety Valve?
Answer: Irrespective of their design, safety valves are calibrated to a specific set pressure. This set pressure is determined considering various factors such as the type of medium contained within the vessel and the requirements of the specific safety application. When pressure reaches the predetermined set point, the safety valve activates, allowing the medium to be discharged in a controlled manner, effectively averting any potential overpressure hazards.