The journey into the world of industrial automation begins with a clear understanding of what a PLC Panel is. At its core, a PLC Panel stands for Programmable Logic Controller Panel, and it’s an indispensable component in the realm of automation and control systems.
Picture it as the brain of industrial processes, capable of making decisions, executing tasks, and ensuring that machinery and systems function efficiently and reliably. But how does it do this?
The ability to replace human intervention in complex and repetitive tasks with precision and consistency makes PLC Panels the cornerstone of industrial automation. Whether it’s on a manufacturing assembly line, a chemical processing plant, or even in building management systems, PLC Panels play a pivotal role in optimizing operations.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a PLC Panel?
A PLC panel is a dedicated steel enclosure housing the essential electrical components needed to operate machinery or control industrial processes within a factory. The term “PLC” stands for Programmable Logic Controller, which refers to a robust industrial computer typically situated within these control panels.
To truly grasp the essence of a PLC Panel, it’s crucial to understand what lies at its core: the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC).
Definition and Function of PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)
A PLC is a specialized computerized device designed to control and automate various industrial processes and machines.
Definition
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is an electronic device equipped with a microprocessor that executes control functions based on a set of user-defined logic. It operates by continuously monitoring inputs, processing them according to a program, and producing corresponding outputs to control machinery and industrial processes.
Function:
The primary function of a PLC is to replace human intervention in repetitive and complex tasks with precision, consistency, and speed. It accomplishes this through the execution of a pre-programmed logic, making it ideal for a wide range of applications in industrial automation.
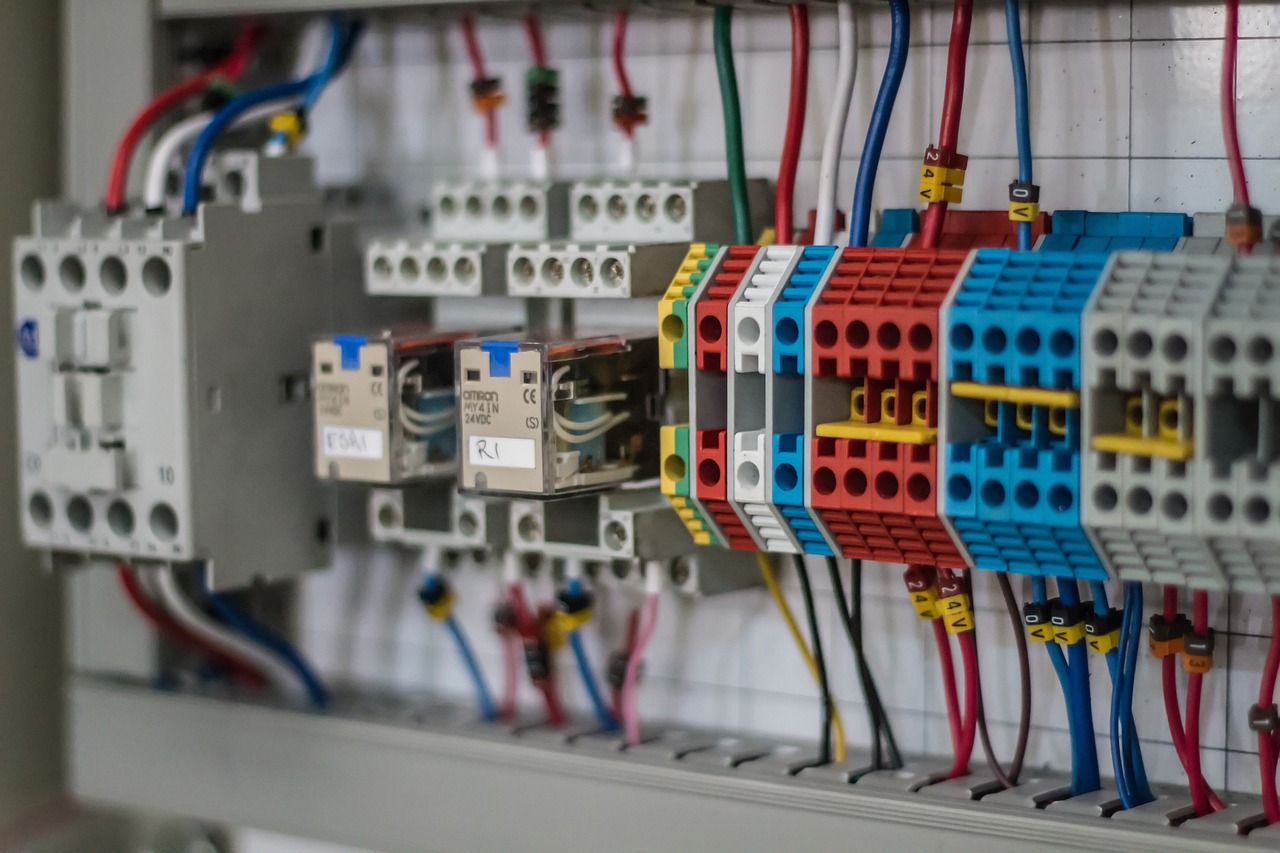
Components of a PLC Panel
Now, let’s break down the key components that make up a typical PLC Panel. These components work in harmony to ensure that the PLC functions effectively within an industrial automation system.
In a PLC Panel, you’ll find two distinct categories of components: Control Components and Power Components.
Control Components of a PLC Panel
PLC Hardware:
The hardware component of a PLC includes the physical components of the PLC itself, such as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, power supply, and input/output (I/O) modules. The CPU serves as the brain of the PLC, executing the programmed logic, while memory stores the program and data.
Input and Output Devices:
These devices serve as the interface between the external world and the PLC. Inputs are signals from sensors or other devices that the PLC monitors, while outputs are signals sent to actuators, motors, or other devices to control industrial processes. Input devices may include sensors for temperature, pressure, or motion, while output devices could include motor starters, solenoids, or relays.
Communication Interfaces:
Communication is key in industrial automation, and PLC Panels are no exception. Communication interfaces enable PLC Panels to connect with other devices, controllers, and even higher-level supervisory systems. This connectivity is vital for exchanging data, receiving commands, and facilitating remote monitoring and control.
Supplementary Circuit Breaker:
This component serves to safeguard the valuable control elements and devices within the PLC panel by interrupting the electrical circuit in case of faults or overloads.
Human Machine Interface (HMI):
The HMI is a graphical display interface utilized by operators for configuring and operating machinery or processes efficiently.
Input/Output (IO) Module:
This module functions as the intermediary connection point between the PLC and the various components and devices that require control, allowing for seamless integration and communication.
Ethernet Switch:
Employed for facilitating network communication among intelligent devices, the PLC, the HMI, and other critical components, ensuring seamless data exchange.
Master Control Relay (MCR):
The master control relay is pivotal in establishing a safety circuit, promptly disconnecting power from all output devices during emergencies. It is typically paired with a prominent red mushroom-head pushbutton for rapid activation.
Operator Push button:
Located on the front of the panel, this push button enables operators to exert control over the machinery or processes with ease.
Terminal Blocks: These essential components serve as junction points for connecting and splicing internal panel wiring and field device wiring, ensuring efficient organization and connectivity.
Power Components of a PLC Panel
Power Supply:
This component performs the essential task of converting high-power voltage into a safer control voltage suitable for operating common control devices like PLCs or HMIs.
Motor Starter:
The motor starter, also known as a contactor, is responsible for initiating motors, providing them with full voltage and enabling them to run at full speed.
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD):
This type of motor controller possesses the capability to regulate motor speed and monitor various motor parameters, offering comprehensive control over motor operation.
Motor Soft Starter:
A motor soft starter gradually initiates motor operation over time, smoothly accelerating it to full speed, which can be particularly useful in scenarios where abrupt starts are undesirable.
Rotary Switch / Disconnect:
This critical component is where electricians establish connections for incoming power wires. It may or may not incorporate fuses and is operated using a black or yellow handle on the panel’s door, allowing for convenient power activation or deactivation.
Power Distribution Block:
Crafted typically from machined aluminum, this block features larger wire connection points at the top and multiple smaller wire connection points below. It serves the purpose of dividing a larger wire into smaller segments, facilitating their use with various components within the PLC panel.
Branch Circuit Breakers:
These circuit breakers serve as protective measures against short circuits and, in some instances, overloads for each individual load, such as motors, heaters, and other devices.
Transformer:
The transformer plays a crucial role in converting high-power voltage into a lower control voltage suitable for operating common control devices like PLCs or HMIs, ensuring compatibility and safe operation.
NEMA Rating and PLC Panel Material
The primary purpose of NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) ratings is to define the capability of a PLC enclosure to withstand specific hazards and environmental conditions. For instance, a utility company housing delicate electrical systems outdoors in a coastal region might opt for a NEMA 4x enclosure to safeguard against corrosion and adverse weather conditions.
In addition to NEMA ratings, PLC enclosures are available in various materials, which significantly influence their performance and functionality. Here are some of the most common base materials employed by manufacturers:
Carbon Steel:
Carbon steel PLC enclosures are cost-effective and robust but are highly susceptible to rust. Therefore, they are not recommended for use in coastal areas where airborne salt can accelerate corrosion.
Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel PLC enclosures have both advantages and disadvantages. While they are fire-resistant, they tend to be heavier and more expensive compared to other materials.
Aluminum:
Aluminum PLC enclosures, although pricier than plastic variants, offer numerous benefits. They are exceptionally durable, can withstand high temperatures, and exhibit exceptional resistance to corrosion.
Polycarbonate Plastic:
Polycarbonate plastic PLC enclosures are generally more cost-effective than other materials and boast superior impact resistance. They are suitable for a wide range of indoor and outdoor applications.
Watch our video for PLC enclosures
Conclusion: Elevating Your Understanding of PLC Panels and Enclosures
In the journey through this blog, we’ve delved deep into the world of PLC panels and enclosures, uncovering the critical role they play in the realm of industrial automation. We’ve explored their components, functions, and materials, gaining valuable insights into how these essential elements contribute to the seamless operation of industrial processes.
In conclusion, PLC Panels and enclosures are the unsung heroes of modern industrial automation. They enable precision, reliability, and control in manufacturing, energy management, and countless other sectors. Understanding their components, materials, and environmental considerations empowers you to make informed decisions when implementing automation solutions.