Welcome to our exploration of the transformative realm of industrial automation, where communication is the backbone of operational efficiency. In this blog, we delve into the dynamic world of Modbus Gateways.

As industries evolve towards greater interconnectedness, the role of Modbus Gateways becomes increasingly pivotal. In this introductory segment, we navigate through the intricacies of these gateways, shedding light on how they serve as linchpins for efficient data exchange and integration. Join us on this journey as we unravel the capabilities, applications, and the unparalleled advantages that Modbus Gateways bring to the forefront of modern industrial communication.
Table of Contents
ToggleDefinition and Overview of Modbus Gateways
Modbus gateways serve as crucial intermediaries in industrial communication networks, facilitating seamless data exchange between devices employing different communication protocols. At their core, Modbus gateways act as bridges, enabling the translation and interoperability of Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) and Modbus TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) communication standards.
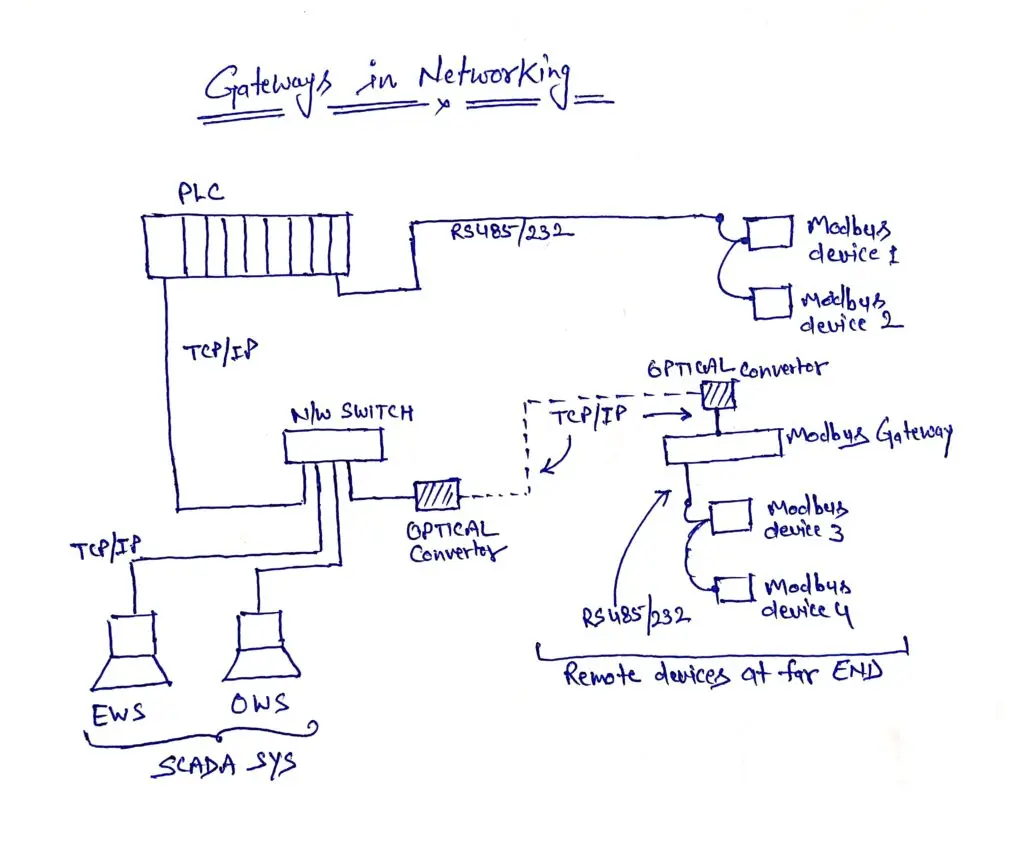
Importance of Modbus Gateways in Industrial Automation
In industrial automation, where diverse devices and systems coexist, the significance of Modbus gateways cannot be overstated. These gateways play a pivotal role in breaking down communication barriers, allowing disparate devices—ranging from programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to sensors—to communicate effectively. By fostering interoperability, Modbus gateways contribute to streamlined operations, improved efficiency, and enhanced overall performance within industrial settings.
Evolution and Adoption of Modbus Communication Protocol
The Modbus communication protocol has undergone a remarkable evolution since its inception. Initially developed by Modicon in the late 1970s, Modbus was designed to facilitate communication between programmable logic controllers. Over the years, its adaptability and simplicity have contributed to its widespread adoption across various industries.
Understanding Modbus Communication Protocol
Brief History of Modbus
Modbus, a time-tested communication protocol, has a rich history dating back to its development by Modicon in 1979. Originally designed for Modicon’s programmable logic controllers (PLCs), Modbus quickly gained traction for its simplicity and efficiency. Over the years, it has evolved into an open standard, becoming one of the most widely used protocols in industrial automation. This section will provide a concise historical overview, highlighting the key milestones that have shaped Modbus into the robust protocol it is today.
Modbus RTU vs. Modbus TCP: A Comparison
Modbus manifests in two primary variants—Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP—each tailored to specific communication needs. Modbus RTU, based on serial communication, utilizes binary encoding and is well-suited for applications where wired connections are prevalent. On the other hand, Modbus TCP leverages Ethernet networks, offering advantages in terms of speed and compatibility with modern IT infrastructure.
Advantages and Limitations of Modbus Protocol
The Modbus protocol brings several advantages to the table, contributing to its enduring popularity in industrial automation. Its simplicity, ease of implementation, and widespread support make it a go-to choice for various applications. However, like any protocol, Modbus has its limitations.
Key Components of Modbus Gateways
Hardware Components
Modbus gateways, serving as the linchpin in industrial communication, consist of several essential hardware components that enable seamless data exchange. Understanding these components is crucial for configuring an efficient and reliable communication network.
Serial Ports
Serial ports are fundamental to Modbus gateways, particularly when dealing with Modbus RTU communication. These ports facilitate serial connections, employing protocols like RS-232 or RS-485. Serial communication is often preferred in scenarios where wired connections are essential, such as in environments with electromagnetic interference. The presence of serial ports allows Modbus gateways to interface with a wide array of legacy devices and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that rely on serial communication standards.
Ethernet Ports
Ethernet ports are integral to Modbus gateways designed for Modbus TCP communication. These ports enable connectivity over Ethernet networks, providing advantages such as high-speed data transmission, scalability, and compatibility with modern IT infrastructure. Ethernet-based Modbus gateways play a pivotal role in facilitating communication in large-scale industrial setups where the use of Ethernet is prevalent. This component ensures the seamless integration of Modbus communication within a broader network architecture.
Power Supply
The power supply is a critical component that sustains the operation of Modbus gateways. Depending on the specific gateway design and application requirements, power supply options may include direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC). Ensuring a stable and reliable power source is essential to prevent communication disruptions and maintain the continuous operation of the gateway. Robust power management is particularly crucial in industrial environments where power fluctuations or outages may occur.
Understanding the interplay between these hardware components is essential for effectively deploying Modbus gateways within industrial networks. Serial ports and Ethernet ports cater to the diverse communication needs of Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP, respectively, while a reliable power supply ensures the gateway’s uninterrupted functionality in demanding industrial environments.
Software Components
Modbus gateways leverage a sophisticated array of software components that play a pivotal role in ensuring efficient communication, data integrity, and security within industrial networks.
#Protocol Conversion : Protocol conversion stands as a foundational software feature of Modbus gateways. It enables the seamless translation of data between different Modbus communication protocols, such as Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP. This capability ensures interoperability between devices that may operate on distinct communication standards. The protocol conversion software within Modbus gateways acts as a bridge, allowing disparate devices to communicate and share information cohesively, regardless of the underlying communication protocol.
#Data Mapping: Data mapping is a crucial aspect of Modbus gateways that involves the intelligent organization and mapping of data between different devices within the network. The software component responsible for data mapping ensures that data exchanged between devices is correctly interpreted and utilized. This feature enables users to define how data from one device should be represented and accessed by another, ensuring a harmonious flow of information across the industrial ecosystem. Effective data mapping simplifies integration and enhances the overall efficiency of industrial automation systems.
#Security Features: In the contemporary landscape of industrial automation, security is of paramount importance. Modbus gateways incorporate robust security features to safeguard communication and data integrity. Encryption protocols, access controls, and authentication mechanisms are implemented to protect against unauthorized access, data tampering, and other security threats. The security software components within Modbus gateways are designed to meet industry standards and compliance requirements, providing a secure environment for critical industrial processes.
The synergy of these software components ensures that Modbus gateways not only facilitate communication but do so in a secure and efficient manner. Protocol conversion and data mapping guarantee interoperability, while robust security features protect against potential vulnerabilities, making Modbus gateways a reliable and integral part of modern industrial communication networks.
Key Characteristic of Modbus gateways
The Key characteristics of this widely used communication device in industrial automation are..
#Open Standard: Modbus is indeed an open standard, meaning that it has been openly published and is not proprietary. This allows users to implement the protocol without paying licensing fees.
#Diverse Electrical Interfaces and Media Support: Modbus and its gateways are designed to be versatile in terms of the electrical interfaces it supports. RS232 and RS485 are commonly used, but it can adapt to other interfaces as needed.
This device is also flexible in terms of the transmission media, allowing communication over various mediums like twisted pair, optical fiber, and wireless connections. This adaptability makes it suitable for a wide range of industrial environments.
#Extensive Industry Support: The mention of over 400 manufacturers and over 600 products supporting Modbus reflects its widespread adoption and support within the industrial automation community. This wide support contributes to its popularity and interoperability.
Types of Modbus Gateways
Modbus gateways come in various types, each tailored to specific communication needs and industrial scenarios. Understanding these types is essential for selecting the most suitable gateway based on the unique requirements of a given application.
#Serial-to-Ethernet Gateways: Serial-to-Ethernet gateways are designed to facilitate communication between devices using Modbus RTU (serial) and Modbus TCP (Ethernet) protocols. These gateways act as intermediaries, converting serial communication to Ethernet and vice versa. This type of gateway is particularly useful in scenarios where both wired and Ethernet-based devices coexist, enabling seamless integration within a unified network infrastructure. Serial-to-Ethernet gateways contribute to the modernization of legacy systems by allowing them to communicate with contemporary Ethernet-based devices.
#Wireless Modbus Gateways: Wireless Modbus gateways introduce flexibility by eliminating the need for physical cables in communication networks. These gateways enable the wireless transmission of Modbus data, providing a practical solution in scenarios where wired connections are impractical or cost-prohibitive. Wireless Modbus gateways find applications in environments where mobility, accessibility, or retrofitting constraints necessitate a cable-free communication approach, offering a versatile solution for industrial automation.
#Multi-Protocol Gateways: Multi-protocol gateways are designed to support not only Modbus protocols but also other communication protocols commonly used in industrial settings. These gateways serve as versatile communication hubs, allowing devices operating on different protocols to interact seamlessly. By supporting multiple protocols, such as BACnet or DNP3, these gateways enhance interoperability in complex industrial networks, providing a unified solution for diverse devices and systems.
Understanding the distinctions between these types of Modbus gateways empowers industrial professionals to choose the most suitable solution based on the specific communication requirements and infrastructure of their applications.
Benefits of Using Modbus Gateways
Modbus gateways offer a range of advantages that significantly contribute to the efficiency, flexibility, and reliability of industrial communication networks. Understanding these benefits is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their processes and enhance overall system performance.
#Interoperability and Integration:
One of the primary benefits of using Modbus gateways is the facilitation of interoperability and seamless integration within industrial automation systems. These gateways act as bridges between devices employing different communication protocols, such as Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP. By providing a common interface, Modbus gateways enable disparate devices to communicate and share data effectively. This interoperability fosters a cohesive and interconnected industrial ecosystem, allowing for the integration of legacy equipment with modern systems.
#Scalability and Flexibility
Modbus gateways contribute to the scalability and flexibility of industrial networks. As organizations expand their operations or introduce new devices, Modbus gateways accommodate the integration of additional equipment without the need for a complete overhaul of the existing infrastructure. This scalability ensures that industrial communication networks can evolve alongside the changing requirements of the organization. Additionally, the flexibility of Modbus gateways allows for the integration of wired and wireless devices, providing adaptability to diverse industrial environments.
#Cost-Effectiveness
Implementing Modbus gateways proves to be a cost-effective solution for organizations aiming to enhance communication within their industrial systems. These gateways enable the coexistence of devices operating on different communication protocols, eliminating the need for extensive hardware replacements. The ability to integrate legacy devices into modern networks through Modbus gateways minimizes the overall cost of upgrading and modernizing industrial systems. This cost-effectiveness is particularly valuable for organizations looking to maximize the lifespan of existing equipment while still benefiting from advancements in communication technology.
#Enhanced Communication Reliability
Modbus gateways contribute to enhanced communication reliability in industrial settings. By serving as intermediaries between devices, these gateways help mitigate issues related to communication barriers and protocol disparities. The protocol conversion and data mapping capabilities of Modbus gateways ensure that data is accurately transmitted and interpreted, reducing the likelihood of communication errors. This enhanced reliability is crucial in industrial environments where uninterrupted communication is imperative for the smooth operation of critical processes.
How to Select the Right Modbus Gateway
Choosing the appropriate Modbus gateway is a critical decision that directly impacts the efficiency and reliability of an industrial communication network. To make an informed selection, consider the following key factors:
#Compatibility with Existing Systems
The first step in selecting the right Modbus gateway is assessing its compatibility with existing systems. Ensure that the gateway supports the Modbus communication protocols utilized by your devices—whether Modbus RTU or Modbus TCP. Additionally, verify compatibility with other protocols that may be present in your industrial network. Understanding the communication standards of your current equipment is crucial to seamlessly integrate the Modbus gateway without disruptions to existing operations.
#Throughput and Performance Considerations
Evaluate the throughput and performance capabilities of the Modbus gateway to meet the data transfer requirements of your industrial applications. Consider factors such as data speed, latency, and the volume of data traffic the gateway can handle. Assess whether the gateway can accommodate the anticipated growth in data demands as your industrial network expands. Choosing a gateway with sufficient throughput ensures that communication remains efficient and responsive, supporting the real-time demands of industrial processes.
#Security Features
Security is paramount in industrial settings, and Modbus gateways should be equipped with robust security features to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access. Look for gateways that support encryption, secure authentication mechanisms, and access controls. Evaluate the gateway’s compliance with industry standards for cybersecurity. A secure Modbus gateway helps safeguard sensitive industrial data and ensures the integrity of communication within the network.
Real-world Applications
Modbus gateways find widespread application across various industries, showcasing their versatility and effectiveness in addressing diverse communication needs. The following real-world applications highlight the practical use of Modbus gateways in different sectors:
#Industrial Automation
In the realm of industrial automation, Modbus gateways play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless communication among programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and other automation devices. These gateways facilitate interoperability by bridging the gap between devices operating on different Modbus protocols, enabling efficient data exchange. In manufacturing plants, production lines, and assembly systems, Modbus gateways contribute to the integration of legacy equipment with modern automation solutions, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
#Building Automation
Modbus gateways are integral to building automation systems, where diverse devices, such as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, lighting controls, and security systems, need to communicate harmoniously. By supporting protocol conversion and data mapping, Modbus gateways enable different devices within a building automation network to share critical information. This promotes energy efficiency, centralized control, and streamlined monitoring, contributing to the creation of intelligent and responsive building environments.
#Energy Management Systems
In the domain of energy management, Modbus gateways facilitate communication between various components of energy systems, such as meters, sensors, and control devices. These gateways aid in collecting and consolidating energy-related data, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis. Energy management systems leverage Modbus gateways to integrate renewable energy sources, manage energy consumption, and optimize overall energy efficiency. The result is improved resource utilization and cost savings for industries and facilities.
#Smart Grids
Modbus gateways play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of smart grids, which modernize the distribution and management of electrical power. These gateways enable communication between smart meters, grid devices, and control centers, ensuring a cohesive and responsive grid infrastructure. By supporting interoperability and data exchange, Modbus gateways contribute to the implementation of demand response strategies, grid monitoring, and the integration of distributed energy resources in smart grid environments.
In these real-world applications, Modbus gateways showcase their adaptability and effectiveness in addressing the communication challenges inherent in diverse industrial and automation scenarios. Whether in manufacturing plants, commercial buildings, energy management systems, or smart grid implementations, Modbus gateways serve as crucial components, enhancing connectivity and facilitating the smooth operation of complex networks.
Use Cases of Modbus Gateways
Successful Implementations of Modbus Gateways
#Manufacturing Optimization:
In a large-scale manufacturing facility, the implementation of Modbus gateways successfully optimized communication between legacy PLCs and modern automation systems. By integrating Modbus gateways, the manufacturing process achieved enhanced interoperability, streamlined data exchange, and improved overall efficiency. This resulted in reduced downtime, increased production throughput, and substantial cost savings.
#Building Management System Integration:
A commercial building management company utilized Modbus gateways to integrate diverse HVAC systems, lighting controls, and security devices within a unified network. The gateways facilitated seamless communication between devices using different Modbus protocols, creating an intelligent and responsive building environment. The successful implementation led to improved energy efficiency, centralized control, and simplified maintenance procedures.
#Renewable Energy Integration:
In a renewable energy project, Modbus gateways played a key role in integrating solar inverters, wind turbines, and energy storage systems. The gateways facilitated communication between devices operating on Modbus TCP and Modbus RTU protocols, enabling real-time monitoring and control. This successful implementation allowed the project to maximize energy production, balance the grid, and optimize the utilization of renewable resources.
Challenges Faced and Solutions Implemented
#Protocol Disparities:
Challenge: The coexistence of legacy devices using Modbus RTU and modern devices using Modbus TCP led to communication challenges.
Solution: Modbus gateways were deployed to bridge the protocol gap, ensuring seamless communication between devices. Protocol conversion capabilities facilitated interoperability, addressing the challenge of disparate communication standards.
#Security Concerns:
Challenge: Increasing cybersecurity threats posed a risk to industrial networks utilizing Modbus communication.
Solution: Modbus gateways with robust security features, including encryption and authentication mechanisms, were implemented. This enhanced security infrastructure mitigated the risk of unauthorized access and protected sensitive industrial data.
#Scalability Issues:
Challenge: The expansion of industrial networks and the addition of new devices led to concerns about the scalability of the existing Modbus communication setup.
Solution: Upgraded Modbus gateways with higher throughput capabilities were introduced to accommodate the growing data demands. This solution ensured scalability, allowing the industrial network to evolve alongside the expanding infrastructure.
Future Trends in Modbus Gateways
Integration with IoT and Industry 4.0
The future of Modbus gateways is closely tied to the ongoing evolution of the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) and the advent of Industry 4.0. Modbus gateways are expected to play a central role in bridging the gap between traditional industrial communication protocols and the requirements of interconnected, smart, and data-driven industrial ecosystems. The integration of Modbus gateways with IoT platforms will enable seamless communication between a broader range of devices, facilitating real-time data exchange and unlocking new levels of automation and efficiency. As Industry 4.0 continues to shape the industrial landscape, Modbus gateways will likely evolve to support advanced IoT architectures, allowing for more intelligent decision-making and predictive maintenance.
Advancements in Security Protocols
The future of Modbus gateways will witness a heightened emphasis on cybersecurity as industries grapple with increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. Advanced security protocols, including encryption standards, secure key exchanges, and more robust authentication mechanisms, will become integral features of Modbus gateways. The focus will be on providing secure communication channels to safeguard critical industrial data and prevent unauthorized access. As industries become more interconnected, security will remain a top priority, driving continuous advancements in the security features of Modbus gateways.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Modbus Gateways
The landscape of industrial communication is continually shaped by emerging technologies, and Modbus gateways are expected to evolve in response to these innovations. Some key technologies influencing the future of Modbus gateways include:
- Edge Computing: Modbus gateways will likely incorporate edge computing capabilities, enabling data processing closer to the source. This approach enhances real-time decision-making and reduces latency, especially in applications where timely responses are critical.
- Wireless Communication: The integration of wireless communication technologies, such as 5G and Wi-Fi 6, will play a significant role in the future of Modbus gateways. This integration will support more flexible and scalable industrial networks, especially in environments where wired connections are challenging or impractical.
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Modbus gateways may incorporate machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence to analyze data patterns, predict system failures, and optimize communication pathways. This integration can contribute to proactive maintenance strategies and further enhance the overall reliability of industrial systems.
As industries embrace these emerging technologies, Modbus gateways will adapt to meet the evolving communication needs of modern industrial environments. The convergence of IoT, Industry 4.0, enhanced security, and cutting-edge technologies is poised to shape the future trajectory of Modbus gateways, positioning them as crucial components in the next wave of industrial communication advancements.
Watch our Video on Modbus Gateway.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Modbus gateways stand as indispensable components in the realm of industrial communication, providing a crucial link between devices operating on different protocols. These gateways facilitate interoperability, enabling seamless data exchange and integration within diverse industrial environments. Whether bridging the gap between Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP or connecting legacy systems with modern automation solutions, Modbus gateways play a pivotal role in optimizing communication networks, enhancing operational efficiency, and preserving the longevity of existing equipment.
As we look to the future, the trajectory of Modbus communication in industrial settings appears promising. The integration of Modbus gateways with emerging technologies, such as IoT and Industry 4.0, opens up new possibilities for intelligent, connected, and data-driven industrial ecosystems. The ongoing advancements in security protocols ensure that Modbus communication remains resilient in the face of evolving cybersecurity threats. Additionally, the incorporation of wireless communication and edge computing capabilities positions Modbus communication for greater flexibility and efficiency, especially in dynamic industrial environments.
To harness the full potential of Modbus gateways and communication protocols, we encourage industrial professionals to embark on further exploration and implementation. Consider the unique requirements of your industrial ecosystem, evaluate the benefits of Modbus gateways in enhancing interoperability and efficiency, and stay attuned to emerging technologies shaping the landscape. As industries continue to evolve, Modbus communication, supported by robust gateways, will remain a cornerstone for seamless connectivity, driving innovation and efficiency across a spectrum of applications.
Resources: www.moxa.com
In the spirit of continuous improvement, we encourage organizations to stay informed about the latest developments in Modbus communication, embrace advancements in technology, and explore opportunities for implementation that align with their specific industrial needs. By doing so, businesses can position themselves to adapt to the ever-changing landscape of industrial communication and ensure the sustained success of their operations.